You’ve probably heard about the dark web, but do you really know what the dark web is, or what it is made up of?
Do you know the risk? Which users are using the dark web? What kind of content is published? Do you know how to safely access the dark web?
You are reading this article now because you are in the largest public part of the Internet (the so-called superficial Internet), but another dark and deep area that is foreign to most users, called the Dark Web. there is .
I will explain today:
What is the dark web?
What kind of content does the dark web have?
A list of risks associated with accessing the dark web.
A secure way to access the dark web.
What is the Dark Web?
The Deep Web and Dark Web consist of all web pages that cannot be identified because search engines such as Google, Yahoo, and Bing are not indexed. In other words, most of these web pages do not contain links from other sites that search engines use as tracking and references for tracking. A specific program is required to access this “cyberspace”.
Many users, and even experts, use the terms Deep Web and Dark Web as if they were synonyms, but there is a fundamental difference between the two. The term deep web or deep internet includes all online resources that are not indexed by traditional search engines such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo. So far, so good.
Despite that, you can access the Deep Web as if it were a conventional website using the standard HTTP / HTTPS web protocol and typical web browsers such as Chrome, Mozilla or Internet Explorer without using any special software. However, accessing the Dark Web requires special browsers and protocols.
On the Dark Web, it is common to use domains with the extension .onion, which indicates an “anonymous” IP address accessible through the Tor network (a tool used to access the Dark Web and “protect the anonymity” of the user while surfing the Internet). If you want to know why we quote the concept of anonymity, read on.
The purpose of the Tor browser and system is to make it difficult to trace both the distributor of the information and its recipient, either to each other or through a third party.
Here is an infographic that represents how Tor works:
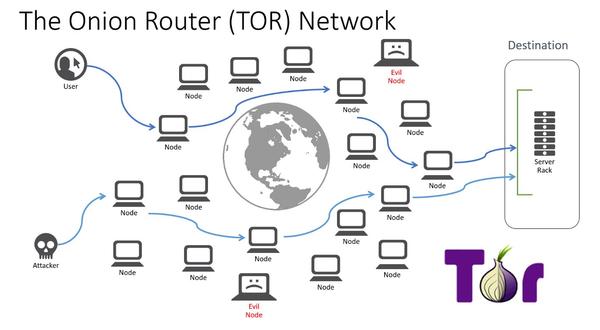
Tor sends user requests through many relays (also known as servers or routers). Generally, at least three relays are used, with the connection between all relays in the network remaining encrypted in layers at all times:
1. The first node-server establishes the user’s connection to the Tor network.
2. The second node-server only knows that the data is coming from the first server, and sends it to the third server.
3. The third node-server only knows that the data comes from the second server-node. And so on. From this last server, also known as the outgoing server, you cannot know the first server-node or the primary origin of the data.
Does Tor guarantee anonymity on the Dark Web?
As cyber-intelligence experts know, Tor’s anonymity is in doubt because “anyone” can install a server on the Tor network (or many) and use it for illegitimate purposes. In the graph, these server-nodes are represented as “Evil nodes”.
Many intelligence services (including Interpol and Europol) and companies involved in organized crime in cyberspace are said to have thousands of server nodes in order to increase the probability that anyone using the network will match several of their server nodes on the same path, and thus be able to decode the connection, its sender, its receiver, and the data being sent.
In addition to these system flaws, there are several factors that can affect privacy and anonymity in Tor:
1. The fact that the source or destination Internet connection may not be secure (the problem resulting from using other people’s networks, which have already been tapped or which leave traceability such as connecting to a Wifi in a Starbacks or an Airport). Otherwise, if you have a very digitalised life, it is possible that your navigation pattern and behaviour can also identify you.
2. The fact that the device used as a sender or receiver is infected by Malware, and you can get the information anyway at the beginning or end of the journey.
3. The fact that the state in which you are may intervene or already has intervened in telecommunications depending on usage patterns, internet searches, etc.
4. The fact that the Internet provider has a policy of storing your usage data, personal data, etc. by default or due to a configuration error. An employee of the said telecommunications company or a cyber criminal who accesses their systems may know your browsing data at source.
What content can you find on the Dark Web?
The Dark Web is the deepest part of the Internet and contains a whole hidden world. The Intelliagg group, in 2015, reviewed more than 1,000 samples of hidden services in Tor and found that 68% of the content on the Tor Dark Web was illegal. Still, while most Dark Web sites are associated with illegal activity, many people use it for legitimate purposes, such as
1. Hide your IP address to protect your privacy.
2. Hide data related to your computer.
3. Hide your browsing data (fingerprint when surfing the Internet superficially), either because you are being persecuted for your political ideas in dictatorial countries, by a criminal organization or for any other legitimate cause.
Below, we explain what you can find on the Dark Web.
THE HIDDEN WIKI
The Hidden Wiki is the checkout for the Dark Web. It is like a “Yellow Pages” or “Teletext” service, since it works as an index of .onion portals accessible from the Tor network. It is very hard to find because, for legal reasons, it is constantly changing servers and domains.
Also, even if you find The Hidden Wiki, you can’t access everything because they restrict traffic with different protection systems, and sometimes you have to receive an invitation. So there is a Deep Web within the Dark Web itself.
By looking at the content map on its home page, we can clarify which websites and services are hidden behind the Tor network:
Financial services: laundering of bitcoins, stolen Paypal accounts, counterfeiting of coins and banknotes, credit card cloning, etc.
Commercial services: black market, sexual exploitation, sale of weapons and drugs, false documentation, among others.
Anonymity and security: instructions for improving privacy in Tor, especially when it comes to selling or transacting in crypto currency.
Hosting services: web hosting and storage of illegal or privacy-enhancing images/files.
Blogs and forums: in addition to those related to buying and selling services, there are two frequent categories that are hacking and exchanging images of all kinds.
Email services: some of the email addresses are free and others are paid with SSL and IMAP support.
Political activism: exchange of censored files, hackitivism and assassination sites. Anarchy and “anti-system” ideology is most prevalent on the Dark Web, but there are many other groups that justify violence.
State Secrets: There is a “section” of Wikileaks and several pages where you can publish secrets, leaks related to the Intelligence Services.
Erotic pages: they are both paid and free access. There is a wide range of subcategories and there is no moral or legal limit.
JOB BOARD FOR CYBERCRIMINALS
There are sites where bad hackers (cybercriminals) promote themselves to carry out illegal activities in exchange for money. These are the two most important sites:
1. Rent a Hacker: a European computer scientist with an alleged 20 years experience in social engineering and illegal hacking who offers users DDOS attacks, zero-day exploits, Trojans and phishing. The minimum amount for a minor job is 200 euros, and from there on, anything you want.
2. Hacker4Hire: in this case, the hacker breaks down his prices by service…
The problem here is to really contrast who is “on the other side” of the connection and their actual experience, so payments are usually made progressively. However, it must be clear that even if these pages exist, they do not necessarily have to be reliable, and most can be perfectly scams.
SCAMMER FAKE SITES
Due to the completely free market, the number of fraudsters is increasing as a result of the immunity that reigns over the dark web. Unlike the superficial Internet, where antivirus can be relied on and the pursuit of cybercrime is more or less effective, precautions are less important on the dark web. Click here to find out how to deal with cyberbullying.
One of the most common scams is an “existing scam” consisting of fraudulent manipulation by a malicious promoter of a cryptocurrency that escapes with investor money during or after an ICO (Initial Coin Offering). .. However, there is a mechanism such as escrow that acts as an intermediary in the process of buying and selling, and if a problem occurs, the store can open a dispute that affects the credibility of the intermediary.
In addition, there are various police and intelligence agencies (public and private). “Honeypots” are fake websites created by security agents to hunt down illegal people.
ONLINE MARKETS
Skil Road is Tor’s most famous brand and is known since 2011 as the Amazon of drugs. However, the FBI found the store’s servers and shut it down. Then Skil Road 2.0 came along and the same thing happened. So, at present, the biggest market for the Dark Web is Agora and, secondly, Evolution. The registration process for both is similar: no need to add an email, just choose a username, a password and a pin to remember.
LIBRARY AND THEORIES
ParaZite is a list of links and texts of anti-system and anarchist ideology. It offers hours of reading through hundreds of text files with fragments taken from images on the Internet, blogs, emails and books.
Onion Chan is a forum open to all users of the Dark Web, where you can post anything. But a very remarkable section is the conspiracy section, in which topics such as healing, aliens, the ways of governments to keep people under control, Holocaust denial, etc. are discussed
How to access the Dark Web safely (and anonymously)
First of all, please note that there is no 100% secure option that guarantees the privacy of your communications. As all cybersecurity experts agree, “if you want a device, connection or system to be secure, turn it off.”
There are certain actions or measures that could increase the security of your communications, such as the following:
1. Create the information or file you wish to transmit on a computer that does not have, has not had, and will not have a connection to the Internet or any mobile or wearable device. Cookies could betray you, here you can see how to delete them. Unless that computer is new or newly formatted, encrypting it with the strongest encryption standards at all times (they vary each time computer capacity or advances in ethical hacking increase)
2. From another computer/device (that may be new or newly formatted, to avoid it having information about you) and that has a powerful antivirus updated, create a virtual machine, and connect from it to the Internet through a secure network that only you control (after verifying that only you have access to the router) using VPN software to ensure an encrypted connection.
4. You can download for the virtual machine the VirtualBox software, a program from which you will have to install the rest of the programs (VPN and Tor).
5. Once VirtualBox is downloaded, you log in and download a VPN to change your IP address and encrypt the connection. Considering the amount of personal data that is collected by many service providers and the lucrative use that is made of this data, it is advisable to take measures to avoid leaving a “trail” when you access the Internet.
6. After accessing the VPN, you need to download the browser called Tor. As we discussed at the beginning of this article, this is a distributed communications network in which the routing of messages exchanged does not reveal the identity of the origin (your IP address) and, moreover, maintains the integrity and secrecy of the information that travels through the network a priori “anonymous”. It is important to note that you will only remain anonymous when visiting websites through the TOR browser (through the Darknet infrastructure).
6. Another aspect to consider is hiding the use of the TOR browser from our Internet Service Provider (ISP). This step is essential as the mere fact of using the TOR browser can be considered suspicious and even illegal depending on the country from which we are connected.
7. When you open the Tor network, you’ll see The Hidden Wiki, from which you can visit the different existing websites. Don’t panic when you see content and links to the .onion domain, and when the URL doesn’t show words, but a mixture of letters and numbers. Moreover, you need to get the .onion links corresponding to the website you want to visit, for which you can use The Hidden Wiki.
8. Finally, it is very important that when you log in you do not download anything at all because you could end up being a victim of a scam or any kind of cyber attack, be it Malware, Ransomware, Phishing, at that time or in the future.











2 thoughts on “Dark Web: how to access, risks and contents”
Comments are closed.